
Why should feudalism be different? Feudalism’s Flawsīefore we go much further, we need to get one thing clear: Feudalism definitely did not exist. There’s not a lot to it.īut that’s actually a big problem - social structures are usually anything but simple. In the year 1000CE, long after Charlemagne’s death, these basic principals transformed into feudalism.

FEUDALISM PYRAMID HOW TO
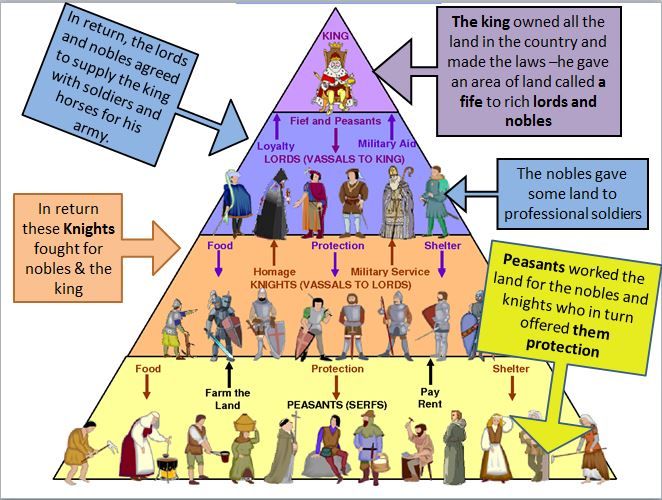
He then came up with the basics of how to spread authority around. The idea is that Charlemagne united a lot of people’s under one banner, and needed to create some way of distributing authority. Which titles were higher or lower varies from country to country, and across different periods of time. Next would be high ranking clergy and royal officials, then the lesser royals whose titles might include Duke and Duchess, Lord and Lady, Count and Countess, etc. While the titles involved may differ, you would expect to see the King and Queen at the top of the pyramid. Land ownership and political authority were passed down the pyramid. Resources and are passed up the pyramid in the form of taxes, physical labor, and military service. When we think of Feudalism today, we imagine a sort of pyramid scheme with the king at the top and the peasant at the bottom.
FEUDALISM PYRAMID FREE
To the best of my ability I have used original and royalty free images and.Every acre of land, forest, person and livestock in.His ‘possessions’ so he knew how much he owned William I commissioned a census (or stocktake) of.
FEUDALISM PYRAMID FULL
Following are sample slides from the full.– Information slides explaining how Medieval Manorialism PowerPoint which is available for This is a sample version of my Feudalism /.The feudal Pyramid of power presentation posters.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
